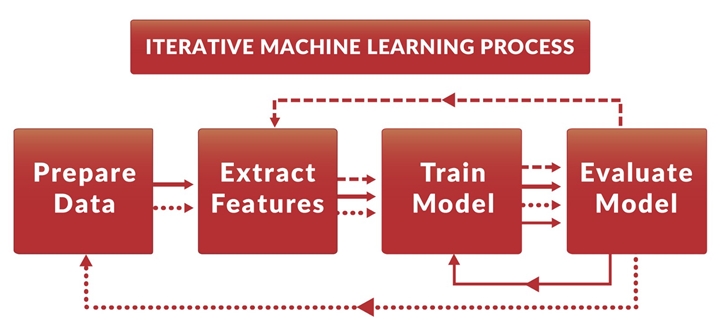
Iterative - Iterations in simple language is Practice. In real life when a student is preparing for an exam at that time if he/she needs a lot of practice, reading, following exercise questions, and providing our answers to understand the subject/ topic. Then n then only we get expertise in that particular concept or you can say area. And if you get more accuracy after practicing then you will get a high rank in that area right. Similar way we need to train our Machine Learning model so that they can be accurate at every time once we deploy them that's why this kind of learning is called Iterative Learning. For this, we need to train our model with different kinds of data set so our model can learn first. The machine also needs to understand data, process it, and produce more accurate output. Most of the time Iterative Learning can be most accurate and faster. At the end of the day, iteration will result in an error-free return in investments.

Comments
Post a Comment